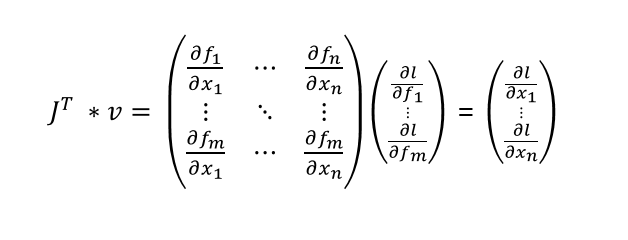Outline
-
Pytorch Tutorial
- Pytorch란?
- Pytorch Tudorial
- Autograd
- Gradient
Pytorch Tutorial
[1/4] Pytorch란?
- pytorch는 파이썬 기반의 오픈소스 머신러닝 라이브러리로, Torch를 기반으로 하고 자연어 처리와 같은 애플리케이션을 위해 사용된다. 페이스북 인공지능 연구집단에 의해 개발되었다. 간결하고 구현이 빠르며 텐서플로우보다 익히기 쉽다.
[2/4] Pytorch Tutorial
empty
- tensor는 자료형의 단위이다.
- torch.empty는 초기화 되지 않은 행렬으로, 그 시점에 할당된 메모리에 존재하던 값이 초기값으로 나타난다.
- type(x)를 출력해보면 자료형이 torch.tensor라고 나온다.
import torch
x = torch.empty(5, 3)
print(x)
print(type(x))out:
tensor([[ 4.8689e-36, 0.0000e+00, 5.6052e-45],
[ 0.0000e+00, 1.4013e-45, 0.0000e+00],
[ 1.4013e-45, 0.0000e+00, -2.0294e+00],
[-3.0359e-01, -6.3788e-01, 1.1869e-01],
[-2.8520e-01, -6.8363e-01, -4.3497e-01]])
<class 'torch.Tensor'>random
- rand 는 0,1 사이에 균등분포에서 랜덤으로 값을 가져와 행렬을 만든다
x = torch.rand(5, 3)
print(x)tensor([[0.7194, 0.6460, 0.8726],
[0.3167, 0.1146, 0.4650],
[0.5900, 0.7723, 0.1102],
[0.3511, 0.8640, 0.3159],
[0.3506, 0.8203, 0.9907]])zeros
- 0 으로 채워진 행렬을 생성
- dtype은 자료형을 지정할 수 있다. (ex. torch.long, torch.int …)
x = torch.zeros(5, 3, dtype=torch.long)
print(x)tensor([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])tensor
- 데이터를 넣어서 텐서를 생성할 수도 있다.
x = torch.tensor([5.5, 3])
print(x)tensor([5.5000, 3.0000])new ones
- new_* 메소드는 크기를 받는다.
x = x.new_ones(5, 3, dtype=torch.double)
print(x)tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]], dtype=torch.float64)randn_like
- dtype을 오버라이드한다.
- randn_like는 사이즈를 튜플로 입력하지 않고 기존의 텐서로 정의한다.
x = torch.randn_like(x, dtype=torch.float)
print(x)tensor([[-1.6818, 1.0321, -0.8268],
[ 0.5849, 0.2614, -1.0141],
[-1.3403, 0.0985, -2.0294],
[-0.3036, -0.6379, 0.1187],
[-0.2852, -0.6836, -0.4350]])size
- x.size()는 x의 크기를 알 수 있다.
print(x.size())torch.Size([5, 3])덧셈
- torch에서의 덧셈연산이다.
- + 연산자와 torch.add()로 연산이 가능하다.
y = torch.rand(5, 3)
print(x + y)
print(torch.add(x, y))tensor([[ 1.1330, 1.1318, -0.0505],
[ 1.3939, 1.1446, 1.4834],
[ 0.0519, -0.4940, 0.8106],
[ 1.4957, 1.4173, 2.0778],
[-0.7459, 0.8813, -0.7525]])
tensor([[ 1.1330, 1.1318, -0.0505],
[ 1.3939, 1.1446, 1.4834],
[ 0.0519, -0.4940, 0.8106],
[ 1.4957, 1.4173, 2.0778],
[-0.7459, 0.8813, -0.7525]])- 아래와 같은 방식도 가능하다.
- 결과를 빈 tensor에 넣어 출력을 한다.
result = torch.empty(5, 3)
torch.add(x, y, out=result)
print(result)tensor([[ 1.1330, 1.1318, -0.0505],
[ 1.3939, 1.1446, 1.4834],
[ 0.0519, -0.4940, 0.8106],
[ 1.4957, 1.4173, 2.0778],
[-0.7459, 0.8813, -0.7525]])- in place 방식이며, 바꿔치기 방식이라고 한다.
# y에 x 더하기
y.add\_(x)
print(y)tensor([[ 1.1330, 1.1318, -0.0505],
[ 1.3939, 1.1446, 1.4834],
[ 0.0519, -0.4940, 0.8106],
[ 1.4957, 1.4173, 2.0778],
[-0.7459, 0.8813, -0.7525]])indexing
- 아래와 같은 indexing은 전체 행에서 1번째 열만 가져오는 코드이다.
- x tensor를 같이 출력해보면 1번째 열만 출력된 것을 볼 수 있다.
print(x)
print(x[:, 1])tensor([[ 0.3303, 0.9045, -0.1993],
[ 0.5441, 0.5543, 0.9550],
[-0.4737, -0.6022, 0.5375],
[ 1.3710, 0.9057, 1.3939],
[-0.9738, 0.0332, -1.4871]])
tensor([ 0.9045, 0.5543, -0.6022, 0.9057, 0.0332])view
- torch.view는 tensor의 크기와 모양을 변경해 준다.
- 4x4로 선언된 x tensor를 view를 사용해 크기를 변경해 주었다.
- view에서 -1은 자동으로 모양을 채워준다.
x = torch.randn(4, 4)
y = x.view(16)
z = x.view(-1, 8)
print(x.size(), y.size(), z.size())torch.Size([4, 4]) torch.Size([16]) torch.Size([2, 8])item
- tensor의 내부 값만 가져온다.
- int형으로 반환해 준다.
x = torch.randn(1)
print(x)
print(x.item())tensor([-1.8750])
-1.874952793121338numpy와의 호환성
- numpy와 형변환이 매우 편리하다.
import numpy as np
a = np.ones(5)
b = torch.from_numpy(a)
np.add(a, 1, out=a)
print(a)
print(b)[2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
tensor([2., 2., 2., 2., 2.], dtype=torch.float64)[3/4] Autograd
requires_grad
- requires_grad의 속성을 True로 하면, 해당 tensor에서 이뤄진 모든 연산을 추적하기 시작한다.
- requires_grad 는 기존의 값을 바꿔치기 하여 tensor 를 변경한다.
x = torch.ones(2, 2, requires_grad=True)
print(x)tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]], requires_grad=True)- requires_grad의 속성을 명시하지 않으면 기본적으로 True가 된다.
a = torch.randn(2, 2)
a = ((a _ 8) / (a - 2))
print(a.requires*grad)
a.requires_grad*(True)
print(a.requires_grad)
b = (a _ a).sum()
print(b.grad_fn)False
True
<SumBackward0 object at 0x7effda51c518>grad_fn
- grad_fn은 연산의 결과로 생성된 것이라는 표시이다.
y = x + 2
print(y)tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)- 추가로 연산을 수행하였다.
z = y _ y _ 3
out = z.mean()
print(z, out)tensor([[27., 27.],
[27., 27.]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
tensor(27., grad_fn=<MeanBackward0>)[4/4] Gradient
grad
- out은 위의 z.mean()의 값과 같다.
- grad를 이용해 변화도를 출력한다.
out.backward()
print(x.grad)tensor([[4.5000, 4.5000],
[4.5000, 4.5000]])야코비안 행렬
- gradient는 스칼라 함수에 대한 일차 미분이지만, 야코비안 행렬은 다변수 벡터 함수에 대한 일차 미분이다.
- 아래 식은 야코비안 행렬을 정의한 것이다.
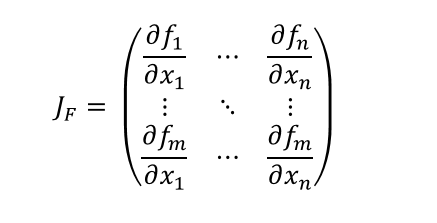
torch.autograd
- torch.autograd는 벡터-야코비안 곱을 계산한다.
- 벡터 v = (v1 v2 … vm)T에 대해 vT * J을 연산한다.